Six Ways Metabolic Health Affects Women’s Health
Introduction
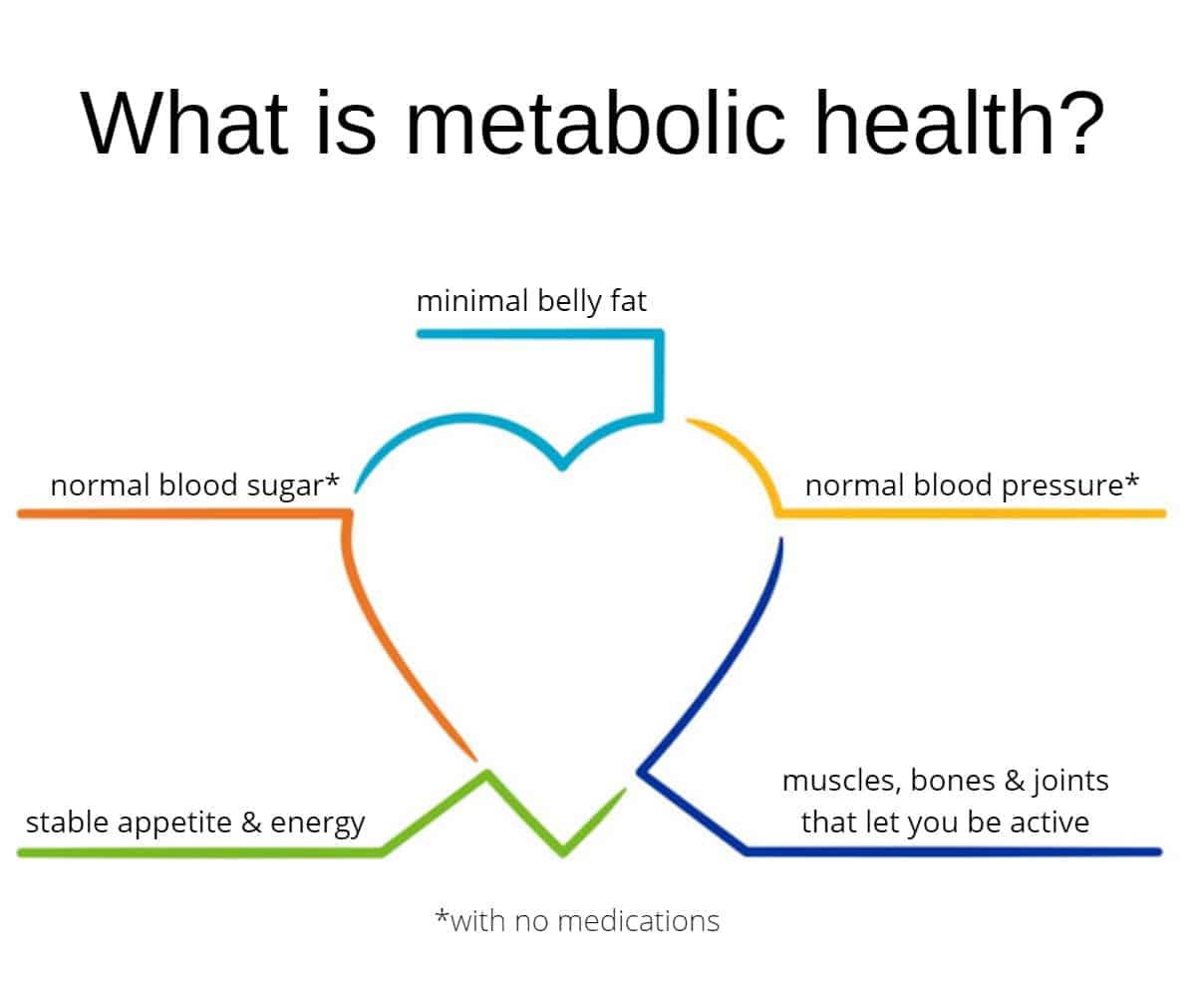
Metabolic health is a term used to describe how well the body generates and processes energy. A healthy metabolism or optimal metabolic health refers to properly functioning cellular mechanisms and energy-producing pathways. Understanding metabolism is crucial for improving and preventing metabolic syndrome and its complications.
Understanding Metabolic Health

Metabolic health encompasses various biochemical processes that occur within the body. These processes include the regulation of blood sugar levels, cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood pressure. When these processes function optimally, the body can efficiently generate and utilize energy.
Why Metabolic Health is Critical for Women
Many chronic diseases arise due to metabolic dysfunction, including obesity, diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and dementia. However, poor metabolic health hits women harder than men. By the age of 45, women are more likely to be overweight or obese, which significantly increases the risk of diabetes. Additionally, women are more prone to impaired glucose tolerance throughout their lives due to factors such as genetics, body fat distribution, and hormonal imbalances.
Factors Affecting Women's Metabolic Health

Genetics: Women may inherit genetic predispositions that affect their metabolic health.
Hormonal Differences: Women experience hormonal fluctuations throughout their lives, impacting metabolism.
Lifestyle Factors: Diet, physical activity, and stress levels significantly influence metabolic health.
Six Ways Poor Metabolic Health Impacts Women’s Health
Infertility
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a leading cause of infertility in women. It affects 4% to 20% of women of reproductive age globally. There is a two-way relationship between hormonal imbalance and PCOS. About 70% of women with PCOS show insulin resistance, and approximately 50% develop type 2 diabetes by age 40, stemming from poor metabolic health.
Hormonal imbalances and high insulin levels directly impact fertility. PCOS leads to increased secretion of androgens (male hormones), which worsen insulin resistance and elevate blood glucose levels. This creates a cycle where androgens further impair insulin activity in muscle and fat cells. However, minor dietary changes can help manage these effects.
Menopausal Symptoms
Hot flashes, experienced by about 80% of women during menopause, are linked to poor metabolic health. Hot flashes can increase the risk of metabolic disorders like diabetes in postmenopausal women by 18%. Menopause brings significant hormonal changes, increasing the likelihood of obesity, insulin resistance, and high cholesterol and triglyceride levels. These changes can elevate glucose levels and disturb sleep during hot flashes.
Poor Skin Health
Collagen and elastin are crucial for skin health. Poor metabolism can impair their function, leading to skin issues. High blood sugar levels, oxidative stress, and inflammation due to metabolic dysfunction can contribute to conditions like psoriasis, acne, and atopic dermatitis. Diets with a high glycemic index can worsen acne by stimulating insulin and IGF-1 production, leading to increased oil production and inflammation. Switching to low glycemic index foods can help mitigate these effects.
Weight Gain
Women, especially those over 45, are more susceptible to weight gain. Insulin levels play a crucial role in fat storage. Elevated blood glucose levels signal the body to store fat. Additionally, decreased estrogen levels during menopause can lead to abnormal weight gain. Maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine is essential for managing weight.
Cognitive Health
Poor metabolic health can lead to cognitive impairments, with women having a higher dementia prevalence than men. High blood glucose levels increase the risk of dementia. Inflammation, triggered by beta-amyloid protein buildup in the brain, contributes to neurodegeneration. Metabolic health issues can impair the blood-brain barrier, leading to cognitive dysfunction. Keeping insulin and glucose levels stable can help prevent these adverse effects.
High Blood Sugar Levels
Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle significantly impact insulin sensitivity. In the luteal phase, progesterone promotes insulin resistance, leading to higher blood sugar levels. In the follicular phase, estrogen promotes insulin sensitivity, resulting in lower blood sugar levels. Adopting a low carbohydrate diet during the luteal phase can help manage blood glucose levels.
Ways to Improve Metabolic Health

Add More Protein to Your Diet
Protein-rich foods boost metabolism by increasing thermogenesis and muscle mass, leading to a higher metabolic rate. Protein also keeps you satiated for longer, reducing calorie intake and helping maintain a healthy weight.
Drink More Water
Staying hydrated boosts Resting Metabolic Rate. Drinking cold water makes the body use energy to bring the water to body temperature, aiding weight loss and improving metabolic health. Green tea and coffee can also boost metabolism, but caffeine should be consumed in moderation.
Get a Full Night’s Sleep
Sleep deprivation can cause insulin resistance and elevated blood glucose levels, components of metabolic syndrome. Poor sleep quality disrupts glucose metabolism, leading to weight gain and hormonal imbalance. Prioritizing sleep is crucial for maintaining good metabolic health.
Don’t Skip Meals
Skipping meals, especially breakfast, can harm your metabolism. Eating a balanced diet that meets your Resting Metabolic Rate is essential. Cutting too many calories signals the body to store fat. A nutritious breakfast boosts metabolism and keeps you energized throughout the day.
Conclusion
A healthy metabolism is vital for overall health and well-being. It sustains basic life processes and prevents metabolic disorders. Women, due to hormonal fluctuations, are at greater risk of metabolic health issues than men. These issues include cognitive impairment, increased blood glucose levels, skin problems, abnormal weight gain, and infertility. Managing these issues through a balanced diet and regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good metabolic health.
FAQs
What is metabolic health? Metabolic health refers to the body’s ability to generate and process energy efficiently, involving the regulation of blood sugar, cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood pressure.
How does poor metabolic health affect women differently than men? Women are more likely to experience hormonal imbalances, higher stress levels, and sleep disturbances, making them more susceptible to metabolic disorders than men.
Can improving metabolic health help with weight loss? Yes, improving metabolic health through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can aid in weight loss and overall well-being.
What are some common signs of poor metabolic health in women? Common signs include weight gain, hormonal imbalances, skin issues, cognitive impairments, and fluctuating blood glucose levels.
How can women improve their metabolic health? Women can improve their metabolic health by consuming a protein-rich diet, staying hydrated, getting enough sleep, and not skipping meals.